- home
- Reference
- Miscellaneous
At the legislative level, orphans are minor citizens of Russia who are left without parents. The death of close relatives is taken into account here.
Often, such children live permanently in social children's institutions (orphanages), from which they can move into families with guardianship. Despite this, the minor will be paid a pension as an orphan, the registration of which occurs in accordance with compliance with the law.
Types of pensions for orphans
An orphan's pension is a social benefit, which is divided into two types. These are transfers due to the loss of a breadwinner and in their complete absence, which can occur as a result of various reasons. On this issue, for example, there are situations when a child is found, but the parents have not been identified.
For the loss of a breadwinner
A survivor's pension is transferred to orphans when both parents have died. This type of insurance is also called “labor”. Payments are made based on the fact that the deceased citizen was previously employed - one working day is enough to calculate the pension.
If parents are unknown
If the parents of a minor child are unknown, based on Federal Law No. 162 of July 2020, he has the right to receive a pension as an orphan. The amount is calculated according to cases where both relatives die.
Reference! If the child is under guardianship, he continues to receive pension contributions, which are transferred to his personal bank account. If a minor is officially adopted, payments stop. Termination occurs on the first day of the next month after registration of “parenthood”.
What is a survivor's pension?
The concept of survivor's pension includes many nuances, only there are several types of pensions (insurance, social, military), so first let's understand the basic terms.
The breadwinner is legally considered an able-bodied family member who provides for his relatives.
Dependents are considered to be relatives of the deceased who require financial support by law: either from the insurance pension of the deceased or from public funds. Dependents include disabled parents of the deceased (pensioners and disabled people), children under 18 years of age, and a non-working spouse.
Depending on whether the breadwinner worked or not, whether he was military or civilian, an appropriate pension will be assigned to his relatives. The pension is state support, its task is to help relatives left without a breadwinner.
Example:
The family consists of four people: father, mother and two children. The father (breadwinner) dies in an accident, the mother is left alone with the children (dependents, but with nuances). According to the law, if the mother was fully supported by her husband, that is, she did not work anywhere, then she has the right to apply for a survivor’s pension for herself and her children. But if she worked and is working, then she is not considered a dependent and only children can receive a pension. If the children are under 14 years old, then the pension will still need to be applied for in the name of the mother as the legal representative; upon reaching the age of 14 years, the child has the right to receive payments himself.
If a woman worked during her husband’s lifetime and, say, for some time after his death, but then quit or was fired, she is not entitled to a survivor’s pension, since she is not considered a dependent. She had to be disabled at the time of her husband's death and be his dependent.
Survivor's pensions are regulated by the following laws:
- Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 400-FZ (as amended on March 6, 2019) “On Insurance Pensions” provides a detailed explanation of who can receive a survivor’s pension and on what grounds;
- “On state pension provision in the Russian Federation” dated December 15, 2001 No. 166-FZ;
- On pension provision for military personnel and members of their families dated February 12, 1993 No. 4468-1.
Features of benefit assignment
At the legislative level, orphans are those minors who are left without parents due to various reasons. These may also be situations related to deprivation of parental rights. But children who have lost close relatives as a result of legal proceedings acquire the right to receive benefits and allowances. In this case, pensions are not paid to the orphan.
The following minors can apply for orphan pensions:
- Those who have lost their parents must be declared dead. When relatives die, the minor's official representative obtains a death certificate from the registry office.
- Parents are unknown . Guardianship authorities, in accordance with Articles 16 and 19 of the Law “On Civil Status Acts” No. 143 of November 1997, must register the found child in the registry office within 7 days from the date of discovery. During registration, information about parents is not entered, so he is automatically recognized as an orphan.
- Parents are missing . This is a difficult situation from a legal point of view. Here Article 45 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation comes into force. Based on the legislative act, searches must be carried out for 5 years, after which they are declared dead in court. Only after this the child becomes an orphan and begins to receive a pension.
The situations when a child is recognized as an orphan are different. Each is considered individually.
Explanatory note to bill No. 961691-7
The authors of this initiative in the explanatory note to the bill noted that people who have reached the age of 75 are classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as elderly. People over 75 years of age almost all have chronic diseases, and in many countries around the world they are paid additional payments and provided with more significant social support measures.
The explanatory note also notes that financial resources have already been accumulated that can be used to increase the level of pension provision for persons who have reached the age of 75.
If the above bill is adopted, this law will come into force on January 1, 2021.

Conditions for appointment
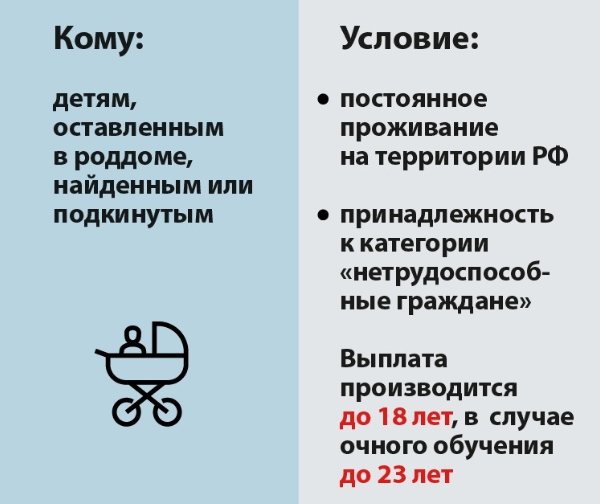
Pension accruals for orphans are regulated by Federal Law No. 166 of December 2001. According to the presented legislative act, benefits are assigned to minors and disabled children who live in Russia but do not have parents due to various reasons. The category of disabled children who also became orphans is considered separately. They are provided with additional benefits and allowances.
Other conditions for appointment include:
- benefits are transferred for the entire period of incapacity for work of the minor;
- the survivor's pension is paid only if the deceased was officially employed, at least for 1 day;
- the orphan should not be involved in the death of his parents - the minor did not commit illegal actions against his parents, which led to their death;
- there is no need to prove dependency - it is enough to provide a birth certificate with “dashes” in the maternity and paternity columns or a death certificate of the parents.
Since the orphan has an official representative in the person of the guardian or employees of the social institution in which he lives, they are the ones who deal with the issue.
Who is entitled to it?
Disabled family members of a deceased person who were his dependents are able to become the owner of a survivor's insurance pension. As we have already said, in this case the family of a missing person is equal to the family of the deceased.
Transfer of a pension is not made if the person entitled to the pension committed an intentional act against the breadwinner, which resulted in his death. His guilt must be confirmed by a court.
Kinds
There are two types of survivor benefits:
- social;
- insurance
Persons who are able to claim their rights to one or another type of payment differ.
Social
Social benefits are assigned in the case where the breadwinner did not have insurance coverage. Also, this sum of money is transferred to those dependents who are guilty of committing a criminal offense that caused the death of the breadwinner.
The right to social benefits belongs to:
- children under the age of majority, as well as after 18 years of age, subject to full-time education (up to 23 years of age);
- children of a deceased single mother.
Labor
Currently, the concept of “labor pension” has been replaced by the term “insurance pension”. It is in this regard that it is not the labor pension for the loss of a breadwinner that is now compensated, but the insurance pension paid on this basis.
Conditions for its assignment:
- whether the deceased or missing person has insurance coverage;
- the death of the breadwinner did not occur due to the dependent committing an intentional crime.
Until what age do they pay?
The transfer of a survivor's pension for clothing and other needs is carried out until the person is recognized as incapacitated.
As a general rule, it stops accruing after the dependent turns 18 years old. An exception applies in the situation where he is a full-time student.
In this case, the payment is compensated until completion of training or until the person reaches 23 years of age.
Who is entitled to a municipal long-service pension? Find out from our article. Read about the features of pension provision for judges here.
Receipt procedure
It is easy for an orphan to receive a pension when he has an official representative. If a minor lives with relatives, but they have not formalized guardianship, the documents will not be accepted by the Pension Fund.
Employees of the guardianship authorities who help relatives obtain guardianship for the child can also apply for a pension for an orphan. To apply for a pension, you must submit documents to the Pension Fund.
This can be done in the following ways:
- by personal appeal to the Pension Fund of Russia branch - apply at the place of registration of the minor;
- by filling out an electronic form on the official website of the Pension Fund;
- by personal appeal to the MFC - you can visit any nearby center;
- through the employer - valid for guardians.
If the child is in an orphanage, employees submit an application to the Pension Fund office at the location of the social institution.
For registration, you must prepare the following documents:
- application for assignment of payments - filled out upon application using a sample or in electronic form;
- child's birth certificate or passport upon reaching 14 years of age;
- passport and identity card of the applicant's guardian;
- a social worker’s certificate, if an employee of a government agency submits an application;
- death certificate of the parents, if available - if the child is found, a birth certificate with “dashes” in the maternity and paternity columns is sufficient;
- certificate of family composition - required for the applicant-guardian, which confirms the fact of his residence in Russia;
- bank statement about personal account information.
If any documents are not available, Pension Fund employees give 3 months to prepare and receive them. If provided on time, the pension will be paid from the moment the application for payments is submitted - the child will receive money for all 3 months.
Attention! A certificate of family composition is also required when registering an orphan on the territory of a guardian - it is important to confirm his presence in the life of a minor child.
How and when to apply for a survivor's pension
First you need to collect a package of documents, which includes:
- Certificate of death or missing person.
- SNILS.
- A document confirming family relations.
- Identity card (including a representative if the person entitled to the pension is under 18 years of age).
- Marriage certificate.
- Document confirming permanent registration.
- Papers that confirm work experience.
- Certificate from an educational institution (school, university), if the pension is issued for the child of a deceased breadwinner.
Each specific case requires the collection of an individual package of papers.
As soon as the breadwinner no longer exists, apply for a pension; it will begin to be paid from the day the application is submitted.
If you write a pension application when after death has passed:
- less than 12 months, then the pension will be paid for the previous months;
- more than 12 months, benefits will be paid only for the previous 12 months, regardless of how much time has passed since the death of the breadwinner.
Payment processing procedure
The payment processing procedure may vary depending on the individual case. But the general sequence of actions is as follows:
- First, it is necessary for a minor to obtain the status of “orphan”. This is done in several ways, depending on the situation. First of all, they go to the registry office, where they receive a death certificate for their parents. As a rule, it is drawn up immediately after their death, so the official representative only needs to use the prepared document. If a child is found, he is registered at the registry office with the help of representatives of a social institution - the guardianship authorities. If parents are missing, a death certificate for them can only be obtained by submitting a court decision.
- As soon as the “orphan” status is received , they collect all the documents that were presented above. In this case, it is easier for employees of a social institution - they only need to provide a certificate of the minor’s residence with them. Guardians must prove the presence of a child in their life - for example, submit a certificate of family composition with registration of the minor on the territory of his property. Also, an affirmative document is the mandatory presence of a guardian’s certificate and confirmation from the guardianship authorities that the orphan is living with him (confirmation from guardianship authorities is necessary when registering a child in another territory).
- The official representative needs to contact the bank to open an account for the orphan. Take a statement with information about your personal account.
- With the collected documents, contact the Pension Fund using any of the above methods. Write an application and wait for it to be registered by employees.
Then all that remains is to wait for the payments that will be transferred to the orphan’s personal bank account. The guardian can use the money, but he must present all receipts for purchases for the orphan during the inspection by the guardianship staff.
Employees of the social institution where the orphan lives cannot use the funds. The money will be collected in the minor’s account, which he will be able to use after he turns 18.
Until what age is it paid?
Citizens have the right to an insurance song:
- Child, sister/brother and grandson of the deceased breadwinner, minor;
- The same categories of citizens under 23 years of age if they are full-time students;
- For life, if the pension recipient is assigned the “disabled person” category, which he acquired before reaching the age of majority;
- Until the brother, sister, child or grandchild of the breadwinner, whom the pension recipients are caring for, turns 14 years old;
- Spouses, parents, grandparents (from 55 years old - for women, from 60 years old - for men, with the exception of cases where the pension is assigned 5 years earlier) is assigned for life.
How much will orphans receive in 2020?
In 2020, children who lost one breadwinner were paid 5,283.84 rubles, and orphans - 10,567.73 rubles. In 2020, it is planned to index social pensions by 4.1% from January . This means that the survivor's pension will be 5,500.50 rubles, and orphans will begin to receive 11,001 rubles.
Orphan pensions are significant assistance from the state to minor citizens and their guardians. They can use the funds at their own discretion, but in the interests of the child.
Security benefits for orphans after turning 18
Orphans essentially go into life unprovided for. The state program for supporting orphans is designed to provide full financial support to this category of citizens.
List of financial assistance
Orphans have the right to receive assistance upon completion of their studies at a boarding school or vocational education institution, which consists of providing:
- shoes;
- clothes;
- furniture purchases;
- purchase of other interior items and equipment;
- receiving benefits in the amount of 500 rubles.
The issuance of materials is replaced at the request of the citizen with the provision of monetary compensation.
Public utilities
All benefits in the Russian Federation are divided into federal and regional. The first type includes compensation for the share of utility costs that falls on the orphan before he reaches adulthood.
For such children, a 100% discount is established, but with orphans from 18 to 23 years old, a slightly different picture emerges. Since these people may have their own income (scholarship, salary, etc.), discounts on housing and communal services are provided by individual regions (Moscow, Rostov region) and are not mandatory at the state level.
Education for students after 18 years of age: what is required
The right of orphans to receive education under special conditions is regulated by the provisions of Article 6 of Federal Law No. 159 of December 21, 1996. Let us note that quite serious preferences have been established.
Otchniki
Orphans and persons from among them during their studies (if admitted to universities, technical schools, vocational schools under the age of 23) receive:
- social scholarship in the amount of 50% more than the payment for ordinary children;
- free meals in the canteen or compensation for food, which usually amounts to 2 times the amount of the orphan scholarship;
- annual payment of benefits for the purchase of educational books, stationery, shoes and clothing;
Correspondence students
Unfortunately, all orphan benefits are provided only for full-time education, so when receiving education without permanent attendance at an educational institution, a person:
- may be located in another locality;
- make money because people have time for it.
Benefit after graduating from a technical school or college and upon entering a university
As already stated above, in accordance with the norms of paragraph 1 of Article 8 of Federal Law No. 159 “On additional guarantees for social support for orphans and children left without parental care,” persons in this category have the right to receive assistance upon graduation from an educational institution. We are talking about providing clothes, shoes, furniture for housing, as well as cash payments. Also, upon reaching the age of majority, orphans have the right to receive housing by writing an application to the relevant authorities. It is worth noting that the provision of materials at the request of the orphan is replaced by the transfer of monetary compensation. Payment is provided only once. Information about the provision of assistance is recorded in a centralized computer database, so it will not be possible to deceive the state and receive money again.
Medicine
Persons from among orphans and representatives of the category deprived of parental care receive the following types of medical care free of charge:
- hospitalization in medical institutions;
- receiving surgical and other technological treatment;
- the possibility of receiving treatment in foreign clinics at the expense of the federal budget;
- Providing vouchers for health improvement in a sanatorium.
Travel and flights
Orphans who have lost their parents have the following privileges in the field of transport:
- completely free travel on public transport;
- purchasing a reserved seat roundtrip ticket once a year;
- a similar option for air travel in economy class or traveling by bus.
Individuals deprived of parental care enjoy the right to free travel on city public transport.
A comprehensive list of benefits is given above. Nothing else is provided for by Russian legislation.
Benefits for children

Parents who accept an orphan child into their family often face financial difficulties and cannot provide the child with necessary goods.
Therefore, the state offers benefits to children under guardianship.
To apply for benefits, the trustee must contact the local branch of the social protection authority for citizens. It is worth noting that Moscow has the largest amount of financial assistance in the country. But the amount of the benefit depends on the health of the baby and the number of children in the family.
For example, a disability group is a good reason for increasing the amount of payments. Children under guardianship are provided with free treatment in sanatoriums and a discount on meals in school canteens. Pupils have the right to free travel, alimony, and survivor's pensions.
Housing after 18 years
Children in foster care after 18 years of age are provided with housing by law. And if there is already living space, the wards receive full right to use and dispose of it. Moreover, according to the Housing Code, apartments should be provided to orphans out of turn.

To understand whether a pupil has the right to receive housing, the guardian must:
- find out whether the apartment is assigned to the ward (he is the owner of the property or has the premises under a social tenancy agreement). Such information is contained in the student’s personal file;
- if there is no information on the housing situation, then it is better to contact the guardianship authorities at the place of residence and demand protection of the right to living space. In any case, the child must have an apartment upon reaching the age of 18;
- If the housing is secured, its condition should be assessed. If it is not suitable for living, then the child is put on a waiting list to receive normal living space.
It is better to find out in advance about assigning an apartment to a child in order to resolve this issue before the age of 18.
Free spa treatment and trips to children's camps

Local governments are allocated funds to purchase vouchers to children's camps, recreation centers, and sanatorium-resort institutions for children under guardianship.
Travel is also paid. But the calculation is made only on the basis of the presented tickets.
Such a voucher is issued if there are indications for treatment in a sanatorium. To apply for it, you must write an application for free treatment at a sanatorium-resort establishment and submit it to local authorities. The application is usually also accompanied by a certificate of the student’s health status.
Free meals in schools

The legislation does not establish an exact list of categories of children who are entitled to free meals in school institutions.
The list is formed at the regional level. Depending on the territory, the amount of benefits and the conditions for receiving them may vary.
But after conducting a little research, we can conclude that pupils of foster parents have the opportunity to eat in school canteens for free.
- child's birth certificate;
- documents that certify the presence of a guardian;
- certificate confirming that the child has been assigned a disability group;
- copies of guardians' identity cards;
- application for free food.
A number of other documents may also be required. A complete list should be obtained from the administration of the educational institution.
Budget places in higher education institutions

A child under guardianship has the right to be enrolled in a higher education institution on a budget place.
True, this only applies to state universities. To be accepted into the exam, you must score the minimum possible number of points.
As a rule, 10% of the total number of budget places is allocated to persons under guardianship. Another 2-3% is intended for disabled children.
Therefore, foster families have a great chance of getting a higher education. They are enrolled in the budget department without competition. And this applies to any faculty.










