Material support from the state is provided to those citizens who cannot take care of themselves.
In Russia, special attention is paid to children, since orphans are still a large social group.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 110-56-12 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 317-50-97 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 222-69-48 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
There are several types of pensions for these persons.
To determine what payment a citizen is entitled to, you should study the current legal acts.
Which child is considered an orphan?
These include minors who have lost their parents. This group also includes children who were left without care. Situations that happened to their parents are taken into account as reasons:
- deprivation of rights to a child;
- missing;
- incapacity;
- Commission of crime;
- contracting an incurable disease.
The status of an orphan is determined by the state. Without it, the child will not be able to qualify for the required payments.
Maintaining Compensation
In addition to social benefits, the children of the deceased retain the right to death compensation under civil law. Thus, the Civil Code provides for the liability of the owner of high-risk equipment. He must compensate for the damage caused by such a source, unless he proves that it was not his fault. This burden is borne either by a legal entity or by a citizen who owns the vehicle legally. This rule follows from the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 1079 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Damage to health is fully compensated to those who caused it. This risk can be insured by drawing up an appropriate contract.
To receive compensation, the recipient of compensation submits at the place of residence to the authority in the field of social protection of the population:
- an application (indicating the postal address or details of the account opened by the recipient of compensation in a credit institution), to which the following documents are attached;
- a certified copy of documents confirming the right to payments.
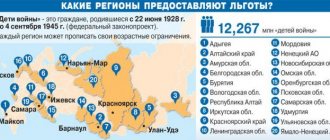
How orphans are supported in Russia in 2020
If children lose their parents, their future fate is determined by authorized persons.
Orphans are sent to boarding schools or assigned guardians (if any). The second option is always a priority for civil servants. They are trying to find relatives who would agree to take care of the children. If the orphaned child is under 14 years old, then guardianship is established over him, if older - guardianship.
The government actively encourages citizens by providing benefits and other benefits so that they have a desire to take orphans into their families.
The legislative framework
Orphan status and the procedure for its appointment are regulated in Federal Law No. 159 of December 12, 1996. This regulatory act describes activities for orphaned children. On its basis, federal and regional laws are issued that determine the direction of the activities of orphanages and boarding schools.
Article No. 5 of Federal Law No. 159 states that funds for social support of minor citizens are allocated from regional budgets. The exception includes children studying in federal institutions.
Regions can develop their own measures to maintain the quality of life of orphans in accordance with the instructions of the Federal Law. In addition, deputies of regional councils are not prohibited from issuing local laws on additional guarantees for child victims.
Also, the legislative framework regulating the protection, maintenance, and provision of orphans includes Law No. 48 of April 24, 2008, Section No. 6 of the Family Code, Articles No. 98.1 and 109.1 of the Housing Code, Articles No. 31-40 of the Civil Code.
Amount of state assistance to orphans
When assigning an insurance pension to orphans, its size will be determined from a combination of the following factors:
- The number of points accrued for insurance periods to the deceased breadwinner;
- Cash equivalent of one point;
- How many parents has the child lost (if the pupil is recognized as an orphan, then when calculating the size of the payment, the scores of the child’s mother and father will be summed up).
Features of calculating insurance coverage for an orphan:
- If the child had only a single mother who passed away, then when the benefit is assigned, her insurance points will be doubled;
- An additional fixed payment may be accrued:
- For orphans – 4 thousand 800 rubles;
- For children who have lost one parent – 2 thousand 400 rubles.
Children applying for a social pension receive it in the amount of 10 thousand 400 rubles.
Preferences for orphans and children deprived of parental care: what is required by law
Orphans are kept by the state.
The support is intended for beneficiaries under 18 years of age, but there are exceptions. If young people receive full-time education, pensions and benefits continue to be provided until the age of 23.
Pension payments
There are insurance, which are assigned in accordance with the parent’s length of service, and social, assigned by regional authorities if the mother and father were not employed.
Parents who have been deprived of their rights to their children by a court are required to pay child support for their maintenance. They are collected from earnings and sent to children's personal accounts.
If parents have no income, the budget pays child support for them.
Education and admission to college, university
To receive them, you need to pass entrance exams and officially become first-year students at a university or college.
Until they receive their diploma, students are paid scholarships from regional funds. The amount is set 50% higher than the amount calculated at the educational institution. The grades obtained at the examination sessions do not affect the payment of the scholarship. While the child is a student, the budget continues to transfer it.
Every year, students receive money to purchase books and manuals. The payment is equal to three times the scholarship.
In addition to monthly mandatory payments, orphans are provided with:
- money to buy clothes, shoes, household items;
- the right to attend preparatory courses free of charge;
- full income for completing an internship;
- clothing, shoes or material payment on the occasion of receiving a diploma.
If a citizen, after receiving a diploma, decides to study for a master's degree, then the benefits are no longer provided.
Housing
Premises for further residence after the orphan is released from the orphanage are provided by the regional authorities.
According to the law, there are two options for providing children with housing:
- If the parents have living space, it is saved for the young heir. Moreover, he himself can live on the territory of the guardian or on his own, but with a legal representative.
- Providing a separate apartment upon reaching the 18th birthday, if there is no inheritance.
The work of the bodies authorized to provide orphans with apartments is controlled by the prosecutor's office. If violations are detected, employees are held accountable.
What financial payments and benefits are provided?
Before reaching the age of majority, the following are provided:
- pension accruals;
- benefits for the unemployed;
- one-time social payment (residents of Moscow).
In addition to material resources, orphans have access to benefits in paying for housing and communal services, landline communications, and receiving a free trip to a camp or sanatorium.
For payment of utilities
The amount of the benefit is equal to 50% of the amount of the receipt for electrical energy, housing maintenance, water, gas, solid waste removal, etc.
During the training period, utility bills will be waived. If the child actually lives in the guardian's area, then the privilege is valid only for the orphan.
One-time payments
Orphans living in Moscow and graduating from educational institutions receive one-time benefits. Dimensions depend on the following situations:
- admission to another educational institution - 20,639 rubles;
- official employment – 79416 rub.
This money is given to orphans, i.e. guardians cannot receive them.
What is dependency
Family members of the deceased are considered dependent on him if they were fully supported by him or received assistance from him, which was their constant and main source of livelihood. Minors who were supported by the deceased receive compensation in the same amount. The child retains the right to a pension and must exercise it before the adoption decision comes into force. But it is actually possible to complete the documents even after. In this case, payments are received by the adoptive parent, being the legal representative of the minor.
Providing disabled dependents with the right to receive insurance payments in the event of the loss of a breadwinner is necessary in order to maintain the stability of their financial situation, since they are not able to independently compensate for material losses due to their disability.
Regional programs
Funds for orphans are allocated from regional and city budgets.
The amount of benefits is established locally and approved by deputies. In other words, the amount of benefits and the list of additional benefits differ in each region. To receive them, you should visit a multifunctional center, pension fund or social security office.
In all subjects of the Russian Federation, orphans have the right to be placed in a preschool educational institution without waiting in line, to visit kindergartens, sports, art, music schools, museums, zoos, exhibitions for free, and to eat free in school canteens.
Up to what age is benefit paid to children left without parental care?
Typically, pensions are paid until the age of majority.
An exception is provided for full-time students. They continue to receive payments until age 23. Moreover, it does not matter what type of property the educational organization has - state, departmental, municipal, private. However, when receiving additional education, benefits do not apply.
Full-time students who have taken an academic leave receive a pension in the usual manner. If they get a job during this time, then pension income is suspended.
Until what age do you pay a pension?
Once an orphan full-time student reaches age 23, payments stop. If he did not manage to graduate from university, the pension will still be cancelled.
The benefit continues to be paid after the age of 23 only to orphans with disabilities.
Procedure for registration by a ward
At the first stage, the following documents are provided:
- guardians' passports;
- orphan's birth certificate;
- current account details;
- statement.
If payments will be sent to the guardian’s account, then the following documents are additionally required:
- decision to appoint a guardian;
- certificate from the ward’s educational institution;
- confirmation of the child’s disability (if any);
- proof of cohabitation with the orphan.
The documents are submitted to the guardianship authority. After consideration, a pension is assigned.
Establishment of maternity and paternity
The origin of the child from the mother (maternity) is established on the basis of documents confirming the birth of the child by the mother in a medical institution, and in the case of the birth of a child outside a medical institution, on the basis of medical documents, testimony or other evidence.
The paternity of a person who is not married to the child’s mother is established by submitting a joint application to the civil registry office by the father and mother of the child; in the event of the death of the mother, her recognition as incompetent, the impossibility of establishing the whereabouts of the mother, or in the event of deprivation of her parental rights - at the request of the child's father with the consent of the guardianship and trusteeship authority, in the absence of such consent - by a court decision.
Help for guardians - what is required by law
The state has provided the following benefits:
- the opportunity not to work at night;
- the right not to go out on holidays and weekends, not to go on business trips (if there are supervised children under 5 years old);
- reduction of work shifts with a decrease in earnings;
- additional 4 days off per month;
- extended vacation by 2 weeks;
- increased tax deductions;
- leave to travel with a child to the place of education and back.
Upon adoption, citizens receive the same financial support as after the birth of a child. The amount depends on the area of residence. When a disabled person is adopted, the benefit increases by 50%.
Adoption of an infant under 3 months or 1.5 years into a family gives guardians the right to receive additional payments.
Features of benefits for disabled people
Orphans with disabilities are paid benefits with various social benefits.
A guardian who cannot work due to the need to care for a child is compensated 60% of the regional minimum wage. Disabled children and their guardians have the right to use transport benefits and receive compensation for operating a car. For persons under 5 years of age with motor dysfunction, a discounted car is provided.
Orphans are entitled to free medicines, prostheses, orthopedic devices, and wheelchairs. Vouchers to the sanatorium are issued, and a sick leave certificate is issued to the accompanying person.
A family in which a disabled person lives pays only 50% of the amount of utilities and a landline telephone. If there is a need to improve living conditions, then the necessary living space is provided without waiting in line.
Disabled children can be educated at home or in commercial institutions.
conclusions
- From July 2020, pensions of guardians of minor children will be indexed.
- Additional social benefits will be sent to pensioners through the chosen method of receiving a pension (Russian Post office, home delivery, MIR card).
- Additionally, there is no need to contact the authorities ; the Pension Fund will independently create lists of pensioner guardians and transmit the information to regional offices. Payments will be received automatically.
- If for some reason the guardian’s pension has not been indexed, you must contact the territorial branch of the Pension Fund.
Author
Breslav Lev Andreevich
Your comments are very important and allow us to identify truly useful materials that are interesting to a wide range of people. Don't forget to rate publications and share your opinion with other site members.
Latest changes to pension payments
In 2020, the Government introduced a new benefit for orphans whose parents could not be identified.
The pension amount is 10,360.52 rubles. Money is paid into bank accounts. Previously, such children were not entitled to survivors' pensions due to their absence in the past. Therefore, the authorities decided to establish this benefit specifically for this group of citizens.
Payments and benefits are assigned only after children are assigned orphan status. In each region they differ in amount and composition. No one has the right to refuse benefits. Children stop receiving pensions and other benefits when they turn 18 (23 for full-time students) or after formal adoption.
Social pension for orphans: what it is and what are its features
Social assistance to orphans is assigned in the case when a minor pupil is left without one or both legal representatives, who are the parents.
A child can be recognized as an orphan if his legal representatives:
- Died or died;
- Declared missing;
- Unknown;
- Lost parental rights;
- Avoid parental responsibilities;
- They refuse to take the child from the social institution where he is temporarily staying.
Within the framework of the law, orphans have the right to claim the following support:
- Depending on the type of assistance (pension):
- Insurance coverage;
- Social Security;
- Depending on the level of subsidy:
- Federal support;
- Regional, municipal.
It is important to distinguish between the categories of insurance and social pensions, since each of these is assigned based on different legally significant facts, including:
- A child left without a parent (parents) has the right to apply for payments in connection with the loss of a breadwinner if:
- The deceased parent (who was also declared missing) was the only able-bodied family member;
- The child, as well as the second parent (if any), are deprived of the opportunity to work for physical and other reasons provided for by law;
- The deceased breadwinner had official earnings from which contributions were made to the Pension Fund (since payments are assigned from the volume of pension savings);
- When considering the relevant application by employees of the extra-budgetary fund, it does not matter whether there was a blood relationship between the pupil and the deceased parent or whether the former was adopted;
- Social pension is paid if:
- It is impossible to provide security for the loss of a breadwinner because the deceased parent has no work experience or his death was the cause of criminal attacks by the child himself;
- The subsidy is allocated from the federal budget;
Even one day of official service of a deceased breadwinner entails eligibility to receive insurance coverage. The length of service also includes non-insurance periods, which include:
- Receiving payments in connection with being unemployed;
- Participation in paid public works initiated by the employment service;
- Travel time to the place of work provided by the employment center;
- Military service;
- Periods for receiving payments provided for temporary disability;
- The period during which the spouse of a serviceman lived in an area where there is no opportunity to work and where the other was sent under a contract;
- Care and education of a child less than one and a half years old;
- Caring for a person with disability group I or aged 80 years.