In order to protect the interests of the insured persons, the government created a special system that guarantees the preservation of all pension savings. Such a system should significantly reduce all risks associated with losses from investing pension savings, as well as with the unstable activities of funds and management companies.
What is a pension savings guarantee system? How does it work and what components does it include? How many non-state pension funds took part in this program? Let's look at these questions in this article.
Pension savings: what it is and how it is formed
Pension savings are understood as funds available in the individual account of a citizen registered in the OPS system of an extra-budgetary fund.
Since the adoption of the federal normative act “on insurance pensions”, these funds have received the status of self-sufficiency.
The funded part of the pension consists of:
- Insurance contributions paid by the employer in accordance with previously effective pension regulations (before the adoption of a number of pension reforms, state old-age benefits consisted of three parts (now there are two), one of which was funded);
- Additional contributions to the funded part (voluntary contributions from citizens and participation in co-financing programs);
- Income from investment activities of the named funds;
- Amounts of money transferred under the assistance program in the form of a maternal certificate.
Peculiarities:
- In the event of the death of a citizen who formed the funded part of the pension, his close relatives or persons mentioned in the law become the legal successors of the funds;
- Pension savings are formed from:
- Funds transferred by the direct owner of the individual account or persons obliged to make such fees in his favor;
- A payment reserve that guarantees the provision of accumulated funds.
Sources of pension accumulation
It is worth talking separately about the sources from which pension savings can be formed:
- insurance for the cumulative share of payment (when the person is insured) refers to:
- people born after 1967,
- women 1957-66 and men 1953-1966 births that created a funded part in 2002-2004, and then stopped doing so due to new amendments to the laws.
- additional insurance contributions, including money that is transferred as co-financing of a pension. Not only an individual, but also an employer or the state has the right to do this.
- Maternity capital (part or all of it).
- Profit from investments of money that has already been transferred.
It is interesting that funds accumulated as a pension, after the death of an individual, according to some laws of our country, must necessarily pass to his heirs.
Guarantee system
The system of guaranteeing payments of pension savings began to operate simultaneously with the adoption of the latest pension reform - in 2015. Its main goal is to protect the reserves formed by citizens and ensure their subsequent payment.
The created system implies two levels of protection, in particular:
- Reserve fund for payments from compulsory insurance;
- Statewide Pension Guarantee Fund (PFGF).
Why the 2013 pension reform resembles shock therapy
The new pension reform, due to its unpredictability and scale, will most likely become a rather memorable event for Russian society. Discussions regarding the main innovations of the pension reform are still ongoing:
- zeroing out the funded pension of silent citizens who did not submit a corresponding application to transfer their savings to a non-state pension fund;
- adoption of a pension formula;
- imposing a moratorium on the transfer of savings;
- withdrawal of pension savings for 2104 in favor of the distribution system.
And these moments shock the average masses.
How the system works
The return of pension savings under the payment guarantee system is carried out upon the occurrence of an insured event, the most likely of which is the revocation of the license of the NPF, the declaration of bankruptcy or the termination of the fund’s activities due to non-compliance with its obligations for other reasons.
If these circumstances arise, the citizen is provided with the following protective measures:
- The safety of savings is ensured by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- Responsibility for payments, their accumulation and increase is assigned to the DIA (deposit insurance agency).
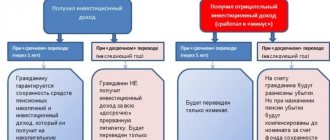
Within three months, after recognizing the case as insured, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation automatically initiates the transfer of funds accumulated by the citizen from the NPF account in favor of the Pension Fund, which assumes obligations for:
- Investing savings and using financial instruments that allow you to increase the initial amount of savings;
- Payment of savings, the decision on which was made before the occurrence of an insured event with a non-state pension fund.
The law allocates funds for pension savings that are considered obligatory for payment . These include:
- Funds allocated under the maternal certificate;
- Accumulated during the operation of the co-financing program;
- Insurance contributions transferred by the employer (with the exception of income from their investment during the period of stay in the accounts of the NPF).
A citizen who has invested pension savings in a non-state pension fund, which is now being forcibly liquidated, can claim to receive investment income from their use, provided for in an agreement with the said institution, only if the sale of his assets ensured debit after the fulfillment of all financial obligations.
If an insured event occurs with a non-state pension fund, the insured person (owner of an individual account) has the right to dispose of guaranteed payments according to the following alternatives:
- Grant the right to manage funds to the Pension Fund of Russia;
- Conclude an agreement and transfer savings to another NPF.
Insurance part of pension
The principle of compulsory pension insurance, which became the basis of the reform, made working Russians insured persons, and their employers - policyholders, paying contributions to the Pension Fund every month for each employee. An insured event is considered to be when a person reaches retirement age, which allows him to apply for its accrual.
A 16 percent portion of the employee’s salary, transferred monthly to the State Fund, is accumulated in the individual’s personal account and becomes a pension in the future. In this case, you can find out the approximate size of the fixed part of the insurance pension before you retire.
The size of the insurance pension is affected by:
- Duration of insurance period.
- Salary (the higher the salary, the higher the insurance premiums and, accordingly, the pension).
- Age. If a person, having reached retirement age, continues to work, then each year of working activity adds a bonus coefficient to the pension.
If you apply for pension payments in 2020, the conditions that the applicant must meet will be: a minimum work experience of 10 years, a minimum number of individual coefficients (points) - 16.2 and, of course, reaching the age that gives the right to retire .
It is worth noting that citizens’ insurance pensions are regularly indexed by the state.
DIA
The Deposit Insurance Agency is the basis of the guarantee system, implementing the following tasks:
- Providing warranty compensation in cases provided for by law;
- Investing funds of fund participants to increase them;
- Collection and control over the receipt of guarantee fees;
- Monitoring activities and taking measures to eliminate unscrupulous participants in the system.
Features of DIA:
- Provides payments in the event of an insured event from a special fund;
- The amount of the provided guaranteed payment includes amounts placed in a special part of the personal account (additional income from investment is not taken into account);
- Forms a register of fund participants and carries out their accounting.
Entry into the DIA is considered mandatory for non-state pension funds. If the agency refuses to include a non-state pension fund in the register, the latter is obliged to cease activities and transfer the existing reserves to the management of the state extra-budgetary fund.
Conditions for including NPFs in the register of the guarantee system:
- Availability of a valid license;
- Successful completion of an audit organized by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- Making mandatory contributions;
- Carrying out the corporatization procedure.
The official website of the agency contains a list of non-state pension funds included in the register of participants in the guarantee system. Among these are (the list is not complete):
- VTB PF;
- Future;
- Lukoil-Garant;
- GAZFOND pension savings;
- Russian Standard NPF;
- NPF Sberbank;
- National;
- KIT Finance;
- HERITAGE;
- Agreement.
What happens to savings in the event of a citizen’s death?
If a person does not live to see retirement, then relatives can inherit the funded part. This is equally true for the situation when a person applied for a lump sum payment of a funded pension, but did not receive it, or even began to receive accumulated funds, but their balance is still a very significant amount (if the option of lifetime payments was not chosen).
When signing an insurance agreement with the fund, a citizen can indicate the composition of the heirs. If he did not leave orders during his lifetime, then the funds are divided in equal shares between legal successors in the following sequence (age and physical condition are not barriers):
- succession of the first stage: children/adopted children, husband/wife, parents/adoptive parents;
- succession of the second stage: brother/sister, grandfather/grandmother, grandchildren.
If in the above categories no one has declared their rights or refused to inherit, then the heirs of the third order become legal successors.

Before six months have passed from the date of death of the insured person, relatives must send applications to the Pension Fund, attaching a copy of the death certificate and providing the documents required to confirm the relationship.
Funds not claimed by legal successors are transferred to the state budget. At the same time, relatives still have the right to apply for the savings of the deceased if, through the court, they can restore the term by proving that they did not apply on time due to good reasons (urgent service, serious illness, long business trip, ignorance of the death of a relative, imprisonment).
Pension Fund under DIA
Guaranteed pension payments are formed within a special fund managed by the DIA, and their accumulation is carried out from the following sources:
- From contributions of NPF participants:
- At the expense of citizens' savings;
- Pension Fund contributions;
- Revenue from investment activities and projects;
- Penalties charged for late fulfillment of obligations by participants.
Key points in forming the fund:
- The law provides for minimum limits on participant contributions and the volume of fund reserves;
- The contribution rate is set/adjusted by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- Payment of premiums is the responsibility of the insurer, the deadline for transferring payment is April 15 of the year following the reporting period;
- For late fulfillment of the obligation to pay the contribution, a penalty is imposed in the amount of 0.1% of the amount of the arrears;
- The accumulated reserves of the fund are distributed in the following areas:
- Payment of guarantee compensation in the event of revocation of a license from a non-state pension fund or the occurrence of another insured event;
- Ensuring the operation of the system and covering the costs associated with it;
- Problems that the fund solves:
- Ensuring the safety of citizens' savings;
- Ensuring compliance with the rights of depositors.
What is the fund made up of?
During the operation of a system that ensures the safety of pensions, the size of the guarantee fund should always increase, because it is replenished with contributions from newly arrived participants who are just entering the system. Thus, the main sources forming the guarantee fund include:
- penalties for failure to transfer funds on time,
- contributions from the Pension Fund,
- contributions from non-state pension funds included in the system,
- profit from investment,
- money and other property received by the Agency after payment of compensation under the guarantee,
- other income permitted by the laws of our country.
NPFs related to the system of guaranteeing pension savings
- UralSib,
- Agreement,
- Future,
- Heritage,
- KitFinance,
- Gazfond,
- VTB,
- National,
- Sberbank,
- Transneft, etc.
NPF activity control system
The current system of supervision and control over the activities of non-state pension funds is mainly built on indirect restrictions and a number of legislative acts obliging funds to comply with the rules established by the state. Among such control measures that directly relate to financial activities are:
- an exhaustive list of permitted assets in which a non-state pension fund can invest pension funds;
- annual audit of financial statements;
- annual actuarial assessment of the fund’s performance based on the sum of indicators;
- monthly (quarterly) operational reporting to the Federal Service for Financial Markets;
- annual publication in the media of the fund's performance results for the past financial year.
In accordance with the law, the activities of NPFs are controlled by: the Federal Service for Financial Markets, the Ministry of Justice, a specialized depository, and so on.
Despite all this, our Russian citizens do not have much confidence in NPFs. To a certain extent, such fears are fair, since the state bears subsidiary liability for the debts of the same Pension Fund - this is directly stated in the law. As for NPFs, until this year they had the status of non-profit organizations with all the ensuing consequences.